Herbivory is a form of predation in which the prey organism is a plant. Plants produce secondary metabolites like phenolic groups terpenoids and alkaloids which help plants to mount a constitutive defense response against the invading pathogen which even include herbivores.
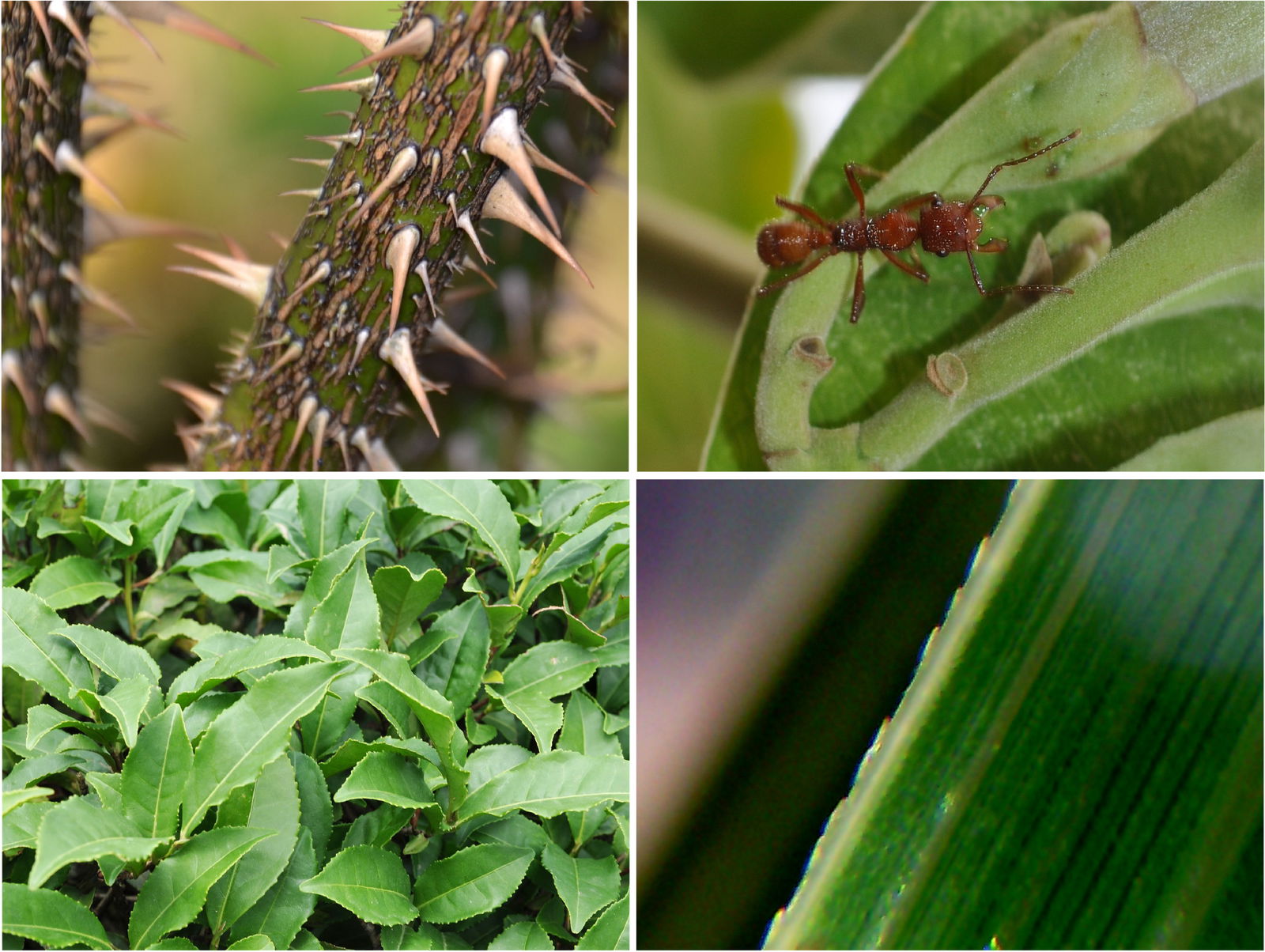
Examples of structural traits include spines and thorns spinescence trichomes.
. B Sharp thorns along with leaves are present in Acacia to deter herbivores. Plants are the necessary part of the biosphere. Plants use substances such as polymers that reduce digestability to avoid being eaten.
They grow and reproduce giving herbivores plant eaters the necessary food for their survival. Plant defense against herbivory or host-plant resistance HPR describes a range of adaptations evolved by plants which improve their survival and reproduction by reducing the impact of herbivores. Pathogens are disease-causing viruses bacteria fungi or protists.
Some of these defense mechanisms are physical like thorns while others are chemical like methylsalicylic acid. Herbivores are dependent on plants for food and have coevolved mechanisms to obtain this food despite the evolution of a diverse arsenal of plant defenses against herbivory. Several plants have evolved various mechanisms both morphological and chemical to protect themselves against herbivory.
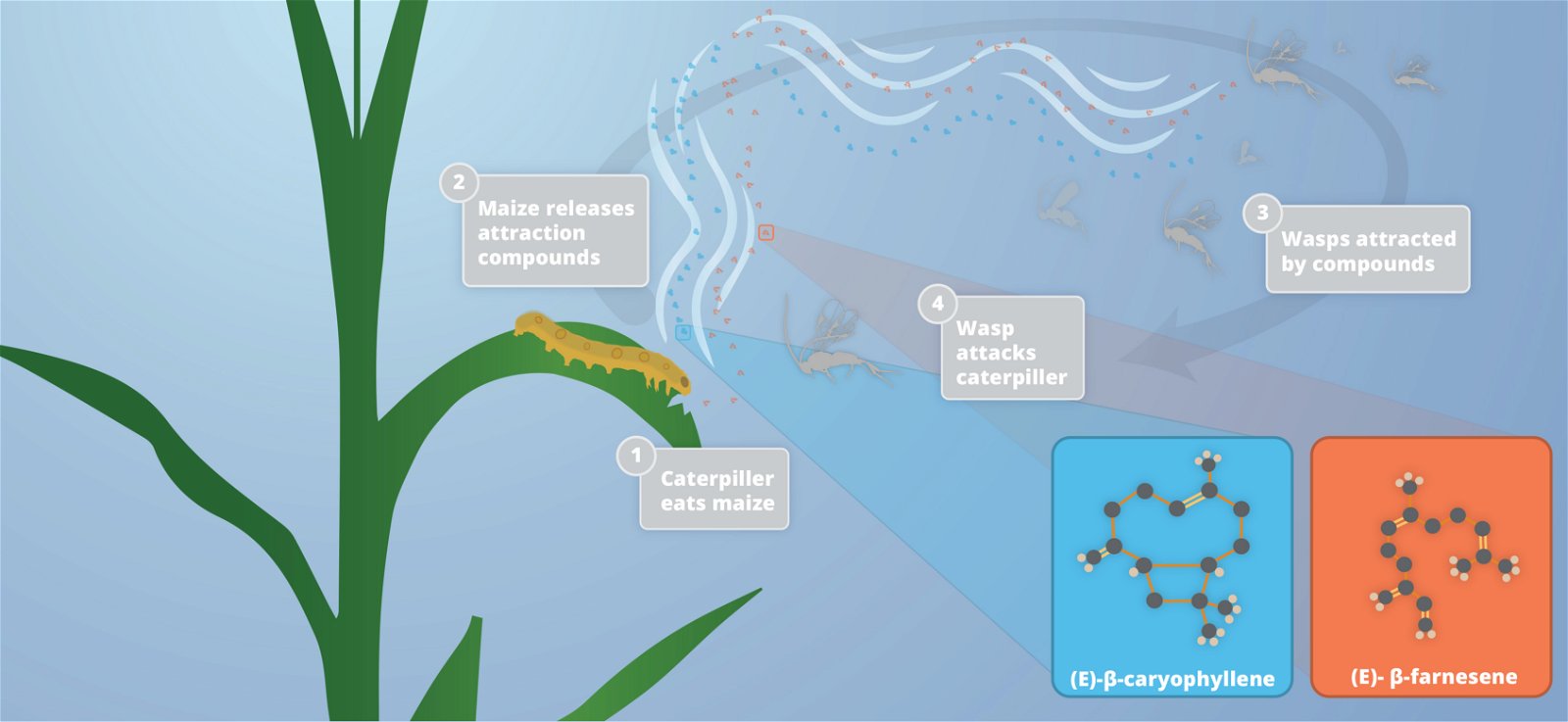
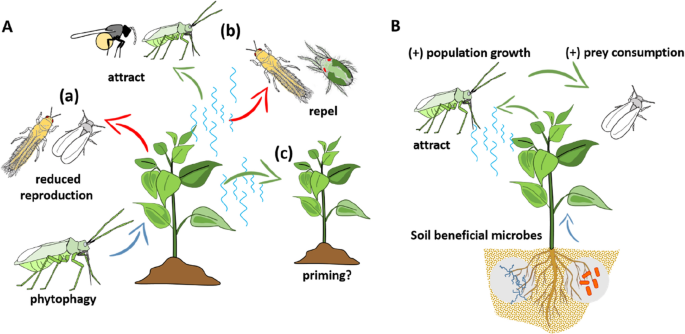
Plants respond to herbivore attack through an intricate and dynamic defense system that includes structural barriers toxic chemicals and attraction of natural enemies of the target pests Fig. These will be briefly discussed here. Plants also use a diverse arsenal of chemicals that ward off herbivores.
The sizes of predator and prey populations often go up and down in linked cycles. The fatal attraction that exists between plants and insects has woven an intricate balance between good and evil survival and devastation and benefits versus harm. Plant Defenses Against Insects.
Herbivores adaptations to plant defense have been likened to offensive traits and consist of those traits that allow for increased feeding and use of a host. Mechanical defenses are the first line of defense for a plant acting to create a barrier against herbivory. With predators being high on the food chain and always on the lookout for a meal prey must.
Plants can sense being touched and they can use several strategies to defend against damage caused by herbivores. These compounds when produced have the. Animals in every biome must eat to survive.
In other cases the impact of these defenses is indirect. Both plants and animals have defense mechanisms against predators. Predation is an interaction in which one organism the predator eats all or part of the body of another organism the prey.
1 Morphological defence mechanisms. 1 9 10 Both defense mechanisms direct and indirect may be present constitutively or induced after damage by the herbivores. Animals use camoflouge and other tactics to defend off predators.
Historically insects have been the most important bane of the plant kingdom. Agricultural Pest That Relies on Bacteria to Overcome Plant Defenses. Some plants have evolved and changed their leaves and the related stipules for two reasons.
Herbivores can highly damage the plant or sometimes completely consume them. Many of these compounds are toxic repelling or even killing grazing herbivores. Stabbiness comes in handy when youre a plant.
Note that some animals such as rattlesnakes and spiders also use venom to capture their prey. As a result plants have evolved many defense mechanisms to protect themselves against the herbivory plant eating. Herbivores are dependent on plants for food and have coevolved mechanisms to obtain this food despite the evolution of a diverse arsenal of plant defenses against herbivory.
Plants have their own ways to defend against predators and pathogens. By Pamm Cooper for UConn Extension. Host plant defenses against insects.
Plants have physical and chemical defences against pathogens. Mechanical defenses include modifications to a plants morphology and are usually one of the more noticeable parts of a plant to humans. Many plants have spines but they are perhaps most memorably marshalled by.
A Cactus leaves Opuntia are modified into sharp spines thorns to deter herbivores from feeding on them. In addition to roses poppies thistle and the porcupine tomato see below also have prickles. Some pathogens infect plants and others infect animals.
Many plants produce secondary metabolites known as. May 27 2021 The oral secretions of herbivorous insects can activate plant defense mechanisms that. The ants feed on the nutritious nectar the plant makes.
A few animals that use venom to defend themselves include. Defense mechanisms are very important to all animal life. In order to check the further invasion by the pathogen the host plants develop some structuresmechanisms which may be defense reactions in the cytoplasm cell wall defense structures defense structures developed by the tissues and ultimately the death of the invaded cell ie.
Most venoms cause the predator to feel a burning pain and some are even deadly. Herbivore adaptations to plant defense have been likened to offensive traits and consist of those traits that allow for increased feeding and use of a host. Plants on the other hand protect their resources.
One example for chemicals being a part of defense response will be phenolic group compounds. For example some plants produce nectar that attracts ants. Herbivore adaptations to defences.
Predator and prey populations affect each others dynamics. Partners in Crime.



0 Comments